Describe What Gregor Mendel Used Pea Plants to Explain
Describe how Mendel used cross- and self-pollination to produce first generation and second generation pea plants explain that Mendel chose pea plants for his experiments because they were easily grown could be cross- self- and artificially pollinated and had obviously contrasting traits outline how Mendels experiments showed. It is an annual plant with a short life cycle.
File Gregor Mendel Characteristics Of Pea Plants English Png Wikipedia
Who was Gregor Mendel.

. Since pea plants self. The pea plant was easy to cultivate and from one generation to next took only a single growing season annual. Mendel performed a series of experiments with pea plants in the 19th century.
Which of the following is responsible for passing albinism from a parent organism to its offspringcells genes proteins nuclei. Mendel chose pea plants as his specimen to study as they exhibit distinctive traits that could be easily observed from one generation to the next eg. Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk who lived in the 1800s.
This species naturally self-fertilizes meaning that pollen encounters ova within the same flower. Mendel studied only on characteristic at a time each time he cross breeder a pea plant. Mendels Crosses Mendels seminal work was accomplished using the garden pea Pisum sativum to study inheritance.
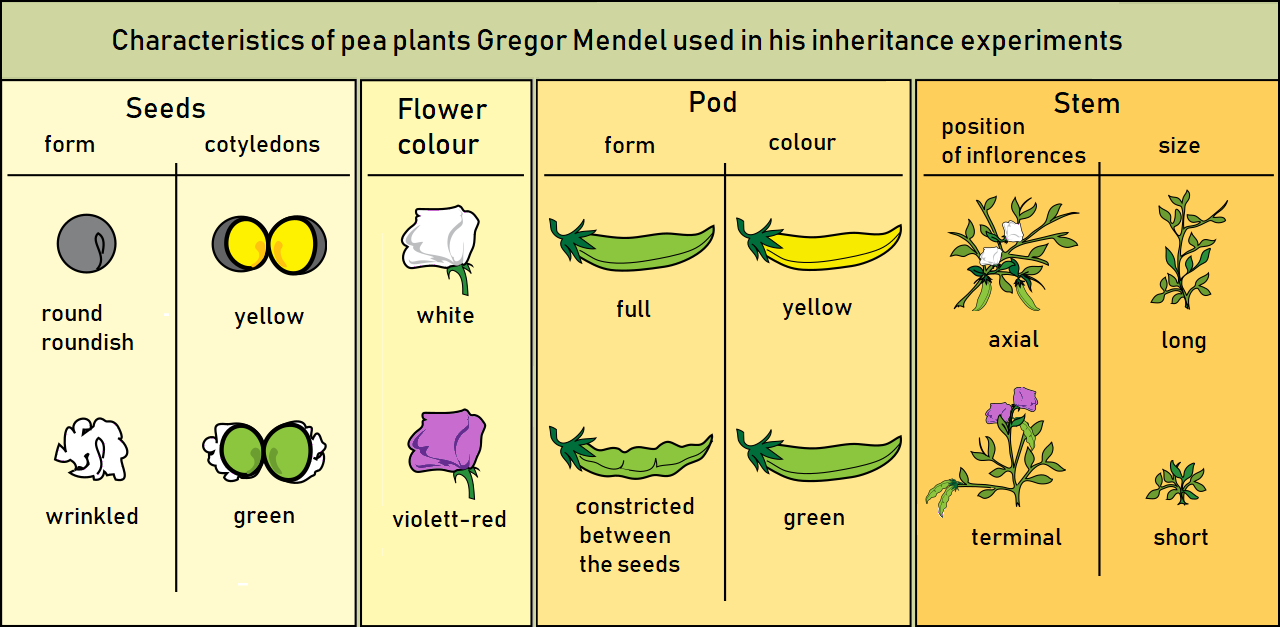
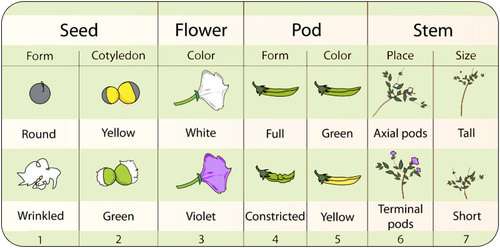
Gregor Mendel is regarded as the Father of modern genetics He was an Austrian biologist scientist and is popular for his garden pea experiment and his laws of inheritance. Inheritance in pea plants Mendel followed the inheritance of 7 traits in pea plants Pisum sativum. Mendel then crossed these pure-breeding lines of plants and recorded the traits of the hybrid progeny.
He combined his knowledge in science and mathematics and observed the number of plants showing traits in his experiment and was able to formulate the law of inheritance. Students will be able to. Gregor Mendel 182284 is an Austrian monk credited with discovering the principles underlying genes and inheritance.
Peas had many sharply defined inherited characters. Mendel is known as the father of modern genetic because of genetic experiments with Pea or Pisum Sativum. In the monastery he set up a series of experiments using pea plants.
Start your trial now. Modern genetics begins with the work of Gregor Mendel an Austrian monk whose breeding experiments with garden peas led him to formulate the basic laws of heredity. Once he had these purebred seeds he mated the two opposing traits for each characteristic.
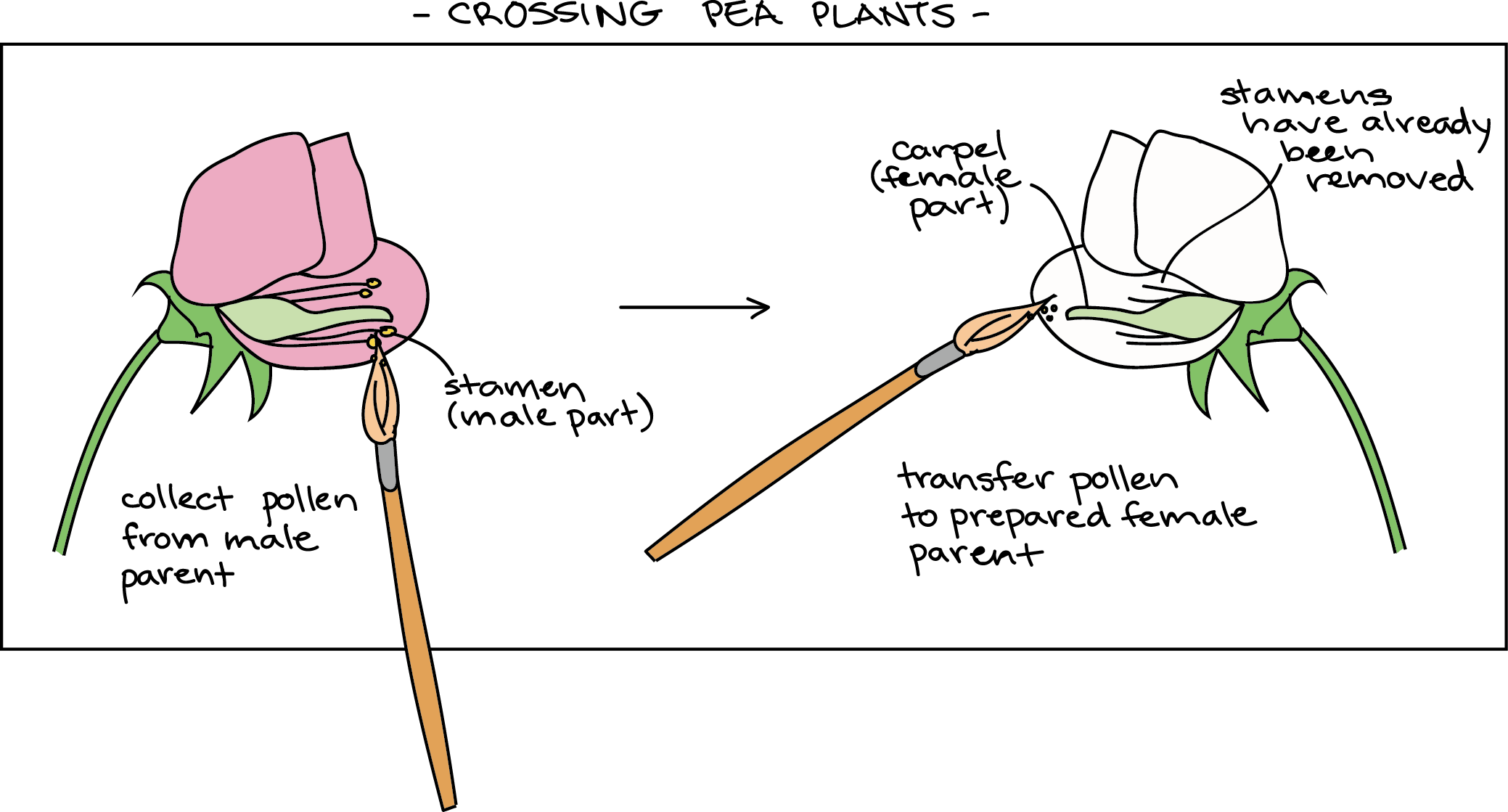
Plants used in first-generation crosses were called P or parental generation plants. Firstly he ensured that each type bred true eg. The self fertilization through many generations helps in easily obtaining the pure line with constant trait in pea plants.
Mendel carried out his key experiments using the garden pea Pisum sativum as a model system. Describe the plant that he performed his research with and explain at least two reasons why this plant proved to be an ideal model species for early genetic research. Mendel collected the seeds produced by the P plants that resulted from each cross.
Consider flipping a fair coin. 1851 Gregor Mendel referred to as the father of genetics. He studied the inheritance of seven different morphologically traits on pea plants.
He used pea plants for 2 main factors. Mendel wanted to investigate the inheritance of traits. At the time the scientific community rejected his ideas and not until these ideas were rediscovered in the 1900s was his work taken seriously.
Since childhood Mendel had been a gardener. -- presence of observable traits with contrasting forms -- produces many offspring in one cross -- short life cycle -- ease in manipulating pollination cross pollination. Let me use an analogy to explain this.
- Easy to grow and produce a large amount of offspring. Mendel observed that pea plants could vary in terms of seven different characteristics. Mendel studied how traits are passed along to offspring.
- Self pollinateMendel could also cross pollinate. The Pea Plant Experiments Mendel used pea plants to learn the genetic basis of inheritance. These led to the discovery of the genetic basis of inheritance the traits that are received by offspring from parents and resulted in him being.
The probability of flipping heads is 5 or 50 the probability of flipping tails is the same. He used only plants that were purebred on homozygous so he could find patterns. Mendel removed the anthers of one pea plant so it.
Pea plants make a convenient system for studies of inheritance and they are still studied by some geneticists today. The flower petals remain sealed tightly until pollination is completed to prevent the pollination of other plants. Why did Gregor Mendel use pea plants in his experiments.
He chose traits that had 2 forms. Mendel conducted hybridization experiments on garden pea. Pea shape round or wrinkled.
Gregor Mendel chose pea plants for his experiments because they are easy to raise have many offspring per mating can fertilize themselves and have varieties in genotype and phenotype that are easily observable. These characteristics make pea plants ideal in the study of genetics and heredity. Gregor Mendel used pea plants to study the inheritance of traits.
In the pea which is naturally self-pollinating this is done by manually transferring pollen from the anther of a mature pea plant of one variety to the stigma of a separate mature pea plant of the second variety. Flower color purple or white. Useful features of peas include their rapid life cycle and the production of lots and lots of seeds.
Gregor Mendel chose the pea plants for his experiments because the garden pea is an ideal subject in the study of genetics for the following reasons. He identified pure-breeding pea plants that consistently showed 1 form of a trait after generations of self-pollination. Soseveral generations can be studied within a short period.
He found that all of the first-generation F1 hybrids looked like 1. Only tall plants yield tall plants. Gregor Mendel used pea plants to study a.
A Reason for the selection of pea plants for the genetic experiments The reason for the selection of pea plants for the genetic experiments are Easy to grow in the garden. Mendel published his findings in 1866 but his discoveries were ignored till 1900 when a number of researchers independently rediscovered Mendels work and grasped its significance. Mendel worked on pea plants but his principles apply to traits in plants and animals they can explain how we inherit our eye colour hair colour and even tongue-rolling ability.
Solution for Why did Gregor Mendel choose pea plants as his experimental organism. Thus they possess many desirable features. The inheritance of traits.
He conducted simple experiments on pea plants to describe the major genetic inheritance principles.
Pea Plants Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation

Leq What Did Mendel Discover About The Passing On Of Traits 9 1 To Ppt Download

No comments for "Describe What Gregor Mendel Used Pea Plants to Explain"
Post a Comment